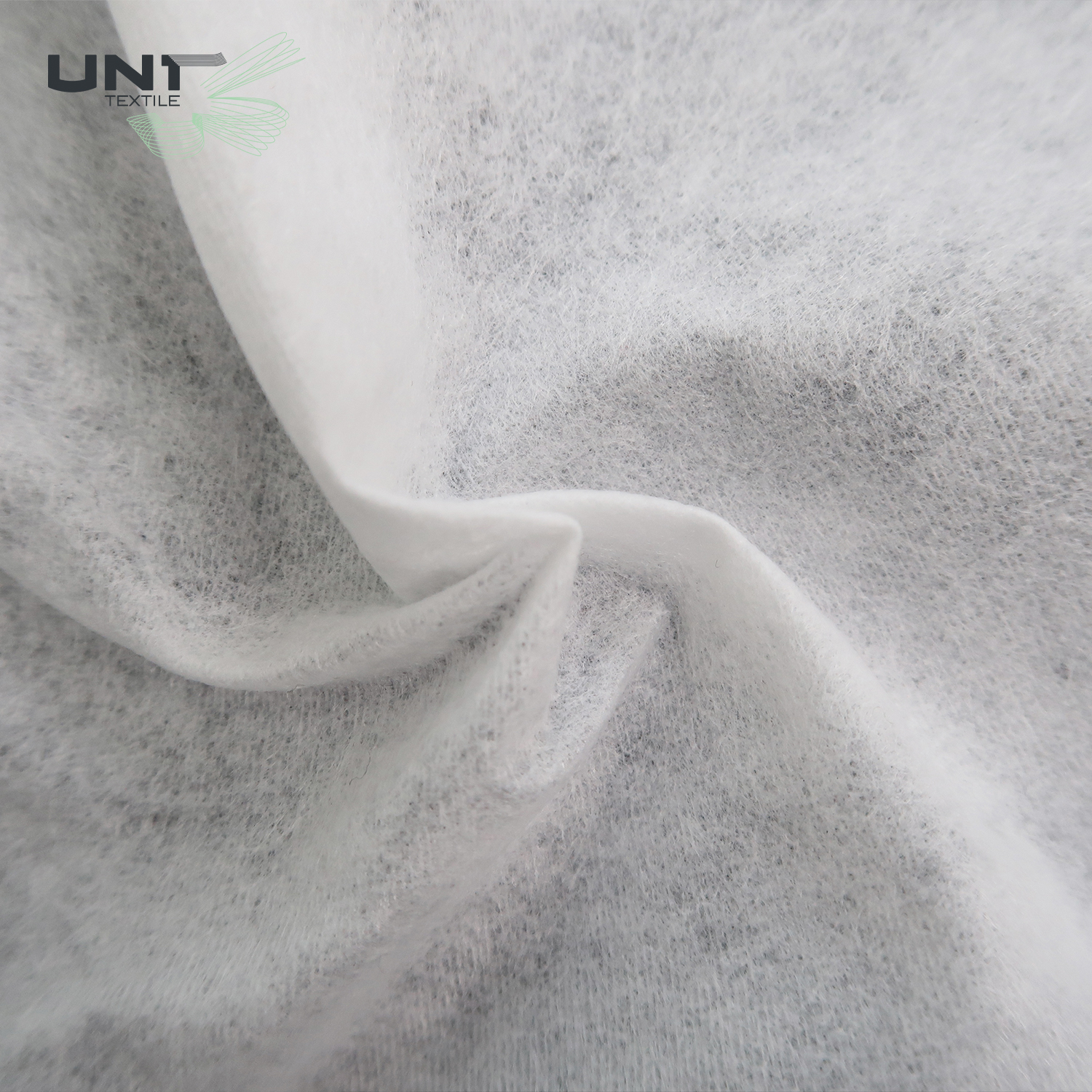
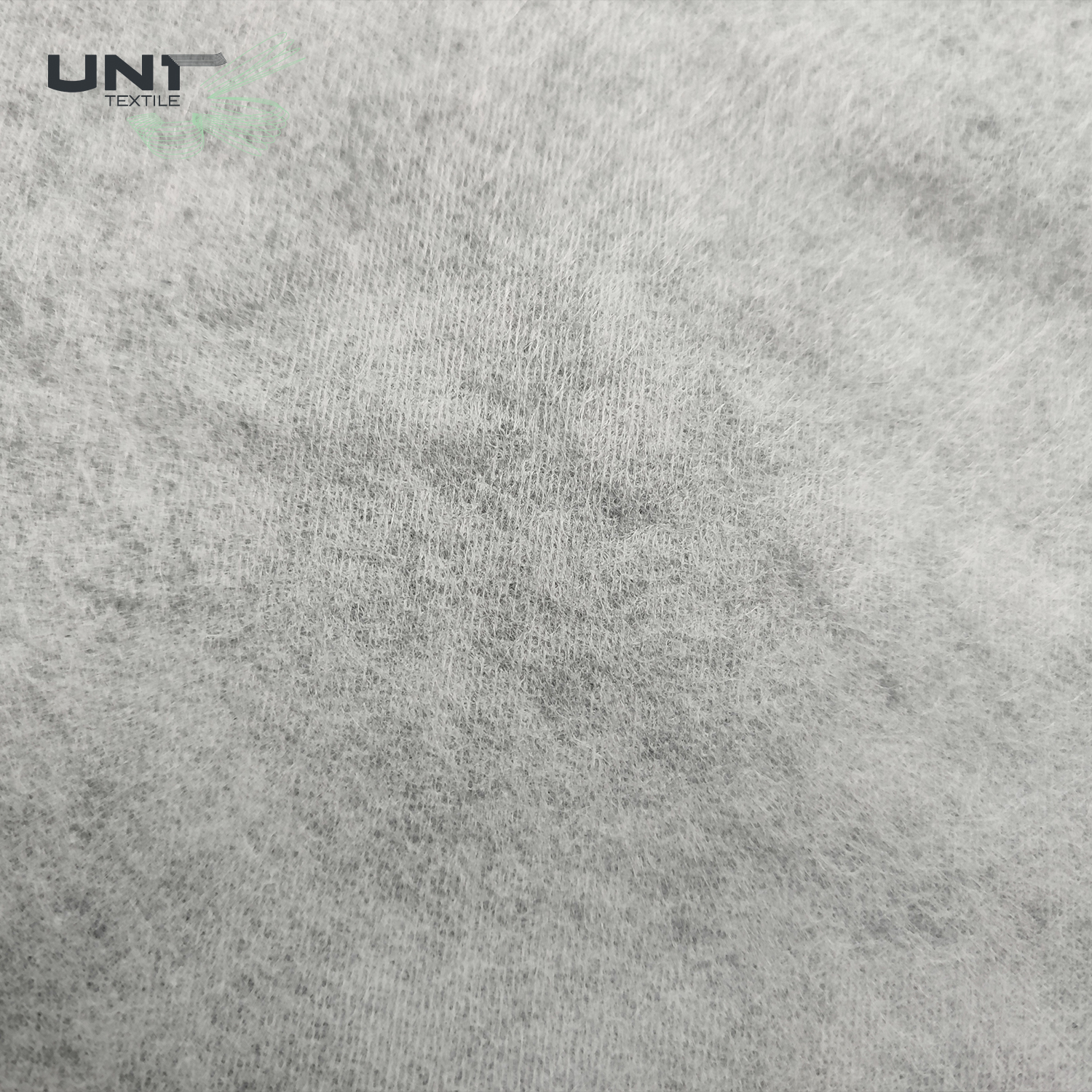
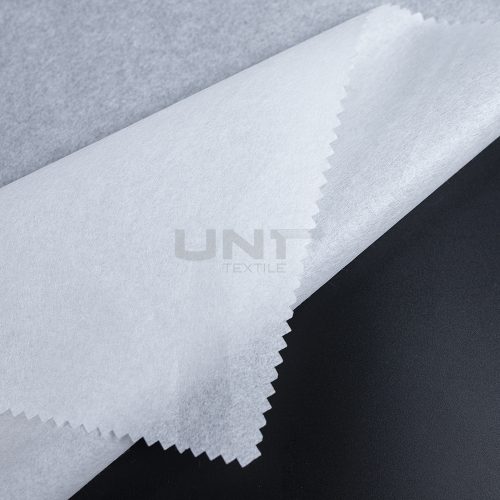
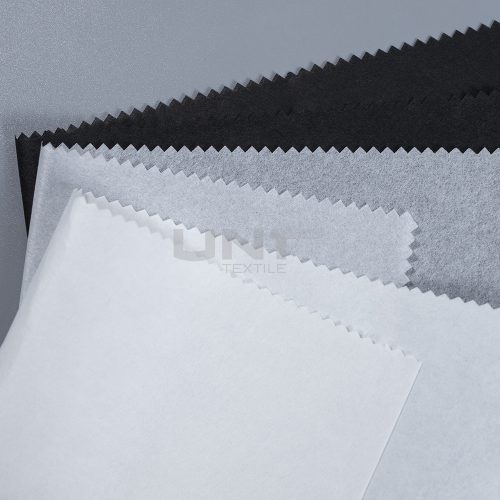
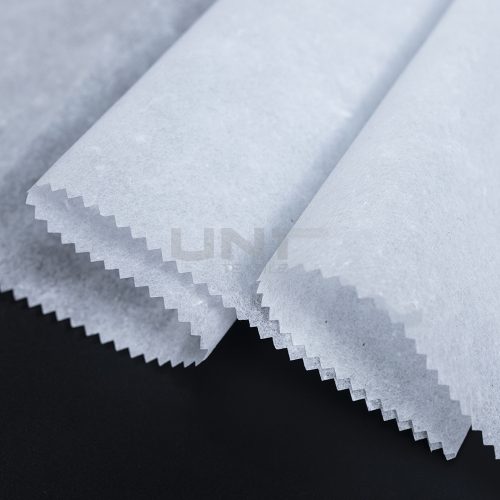
Chitosan Spunlace Nonwoven Fabric
Chitosan spunlace nonwoven fabric is an innovative and sustainable material widely used in medical, hygiene, and cosmetic applications. This unique fabric combines the mechanical strength and soft feel of a spunlace nonwoven with the natural, beneficial properties of chitosan.
What is Chitosan Spunlace Nonwoven Fabric?
Chitosan is a biodegradable and biocompatible polymer derived from chitin, which is found in the shells of crustaceans like. By integrating chitosan fibers or powder into the spunlace manufacturing process, we create a fabric that is not only strong and durable but also inherits chitosan’s natural functions.
product introduce
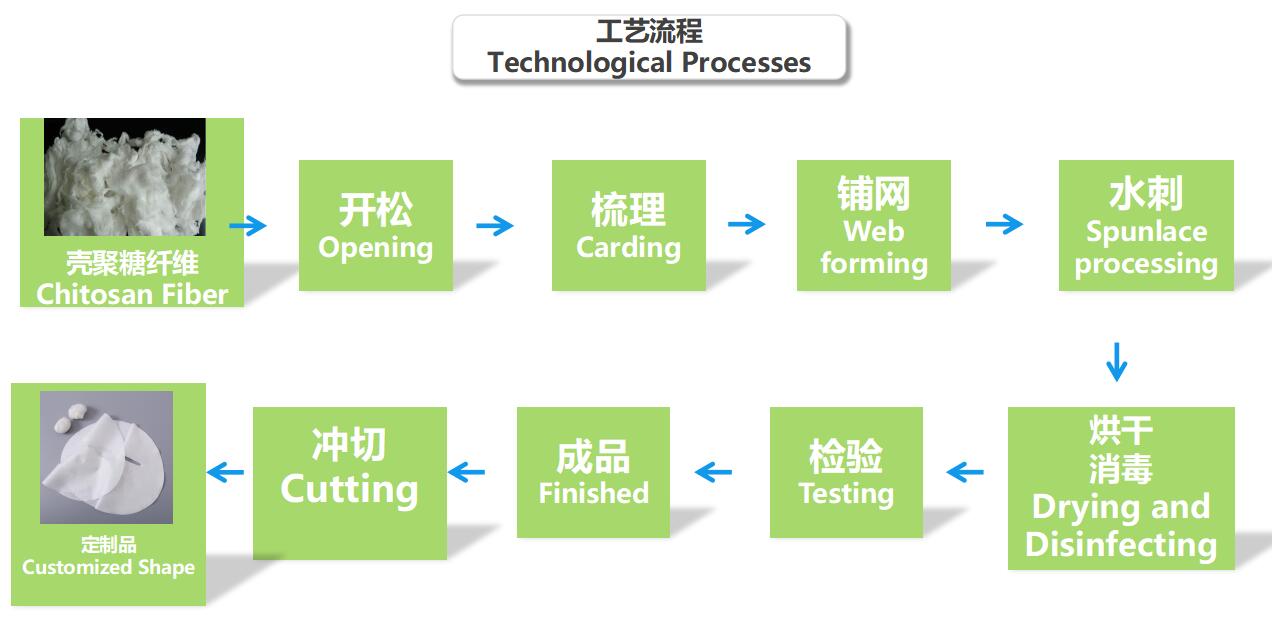
Production Process of Chitosan Spunlace Nonwoven Fabric
The production of chitosan spunlace nonwoven fabric is a sophisticated process that merges traditional nonwoven technology with modern material science. This method ensures the final product is not only mechanically strong but also retains the unique properties of chitosan.
The process typically involves the following key stages:
- Chitosan Fiber Preparation: The first and most critical step is the preparation of pure chitosan fibers. Unlike blended fabrics, this material is produced from a solution of chitosan that is wet-spun into continuous filaments. These filaments are then cut into specific lengths to create staple fibers, which serve as the sole raw material for the nonwoven fabric.
- Web Formation: The pure chitosan staple fibers are then processed to form a uniform, fluffy web or batt. This is commonly achieved through carding, where the fibers are combed and aligned into a web, or airlaying, which uses air to deposit the fibers randomly. The goal is to create a consistent and even fiber structure.
- Hydroentanglement (Spunlacing): This is the core of the spunlace process. The fiber web is passed under a series of fine, high-pressure water jets. These jets act like needles, physically entangling the fibers with each other. This inter-fiber friction and entanglement create a strong, durable, and lint-free fabric without the use of chemical binders or heat, making the process clean and eco-friendly.
- Drying and Finishing: After the hydroentanglement process, the fabric is passed through a drying oven to remove the water. Finally, the dried fabric can undergo additional finishing treatments, such as calendering for a smoother surface or slitting into rolls of the desired width, before being packaged for distribution.
This precise manufacturing method ensures that the final chitosan spunlace nonwoven fabric is soft yet robust, highly absorbent, and ready for use in critical applications where safety, purity, and performance are paramount.
This precise manufacturing method ensures that the final chitosan spunlace nonwoven fabric is soft yet robust, highly absorbent, and ready for use in critical applications where safety, purity, and performance are paramount.
Why Choose Our Spunlace Nonwoven Fabric?
We are committed to providing high-quality, sustainable materials that meet the needs of modern industries. Our chitosan spunlace nonwoven fabric offers a superior combination of performance, safety, and environmental responsibility. If you are looking for an innovative and eco-friendly material for your products, our chitosan spunlace nonwoven fabric is the ideal choice.
additional information
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | 100-500KG |
|---|---|
| Price Range | $120 – $200/kg |
| Delivery Time | DELIVERY TIME 2-4 WEEKS |
| Production Capacity | 150-200 TONS PER MONTH |
| Payment Terms | L/C, D/A, D/P, T/T, Western Union |
Related Products
Stay Ahead With UNT Updates
Shirt collar interlining helps a collar keep its shape, stiffness, and smooth appearance. This article explains the types, materials, and how to choose the right shirt collar interlining.
This article explains cotton interlining, its structure, properties, and why it is mainly used in shirt and collar interlining applications.
This article explains what knitted interlining is, its types, features, applications, and how to choose the right one for different garments.


























.png)